图论及其应用
图论及其应用
对于任意无向图G(输入为矩阵),编写程序实现:
- 任务一:画出图G,并给所有顶点和边标号
- 任务二:求出图G的度序列
- 任务三:画出图G的补图
- 任务四:判断图G的连通性
- 任务五:求出图G的边连通度和点连通度
- 任务六:求出图G的最小点割集和最小边割集(元素最少)
解决方案
任务一(画出图G,并给所有顶点和边标号)
- 通过
BrushTools类中的draw_vertex()# 画点, draw_edge()# 画边, show()# 展示绘制图像方法实现 - 使用二维矩阵接收点和边,点用坐标表示,边用邻接矩阵表示,如下所示:
1 | import numpy as np |
- 使用python绘图库matplotlib实现图的绘制
- 使用matplotlib中的
scatter(x坐标, y坐标, c="颜色")函数绘制图的顶点 - 使用matplotlib中的
plot(x坐标, y坐标, c="颜色")函数绘制图的边,其中边的始点和终点坐标通过邻接矩阵e找到对应顶点坐标矩阵v中相应的坐标 - 通过matplotlib中的
add_artist(plt.Circle((圆心坐标), 半径, fill=是否填充, color="颜色"))函数为画布上添加圆形来表示环 - 使用matplotlib中的
annotate(注释内容, xy=[添加注释的点的坐标], xytext=[注释文字的坐标])注释函数为点和边添加注释。注:在非简单无向图中,平行边通过为一条边添加多个不同的边注释来表示 - 使用matplotlib中的
show()函数将绘制完的图像进行展示
- 使用matplotlib中的
任务二(求出图G的度序列)
- 通过
CalcTools类中的calc_degrees()方法实现度序列的计算 - 因为是无向图,因此点vi的度数只需要考虑邻接矩阵
e中从vi点出发的边的条数,即关注邻接矩阵中的第i行,其中,环提供两度,该方法的主要结构如下:
1 | d_line = [] |
- 其中d_line用来保存最终返回的度序列,当i==j时,说明该边为环,当内层循环结束时,将该点的度数和添加到d_line中
任务三(画出图G的补图)
- 通过
BrushTools类中的draw_complement方法实现补图的计算和绘制 - 先将原图预处理为简单图,遍历邻接矩阵
e,将对角线数字置为0(去环),将其他非0位置的值置为1(去平行边)
1 | for i in range(0, e.shape[0]): |
- 将处理后的邻接矩阵
e中的非对角线位置的值进行非操作,即可获得该图补图的邻接矩阵
1 | for i in range(0, ec.shape[0]): |
- 调用任务一中实现的绘图方法
BrushTools.show()实现补图的绘制与展示
任务四(判断图G的连通性)
- 通过
CalcTools类中的judge_connect()方法判断图的连通性 - 无向图中若任意两点均可达,则为连通的
- 从图中任意一点vi出发,将该点加入连通点列表
v_connect中,判断能否到达其他不在v_connect中的点,即邻接矩阵e的第i行是否有非零数- 如果没有,则说明vi与其他点不相邻,说明该图为非连通的
- 如果有,则说明vi与对应点相邻,进行递归,重复以上过程,继续判断对应点是否能继续走到其他点?
- 完成以上过程后,得到从vi点出发可以到达所有点的列表
v_connect,对其进行处理,判断其中的元素个数是否与该图总顶点数相同,如果相同则说明从vi点出发可以到达所有顶点,该图连通,否则不连通
1 | # 计算图的连通性 |
任务五、六
- 任务五:求出图G的边连通度和点连通度
- 任务六:求出图G的最小点割集和最小边割集(元素最少)
- 任务五和任务六相关,找出最小边割集/点割集,即可获取图的边连通度/点连通度
- 该任务的整体思路为,以找出最小边割集为例,在连通图中从少到多删除图中的边,然后调用任务四中实现的判断图连通性的方法
CalcTools.judge_connect()
或其变体CalcTools.judge_connect_complex()
来判断删除边后的图的连通性,一旦图不连通,则找出一个图的最小边割集,该边割集的大小即为该图的边连通度,该方法的思想同样可以找出所有的最小边割集,此处实现只找出其中一个作为展示- 判断边连通度
- 首先判断输入图是否为连通图
judge_connect()非连通图直接返回空列表 - 第一层循环为删除的边的个数,其范围为1到n-1(n为点的个数):
for num in range(1, self.e.shape[0])- 使用
e2del = list(combinations(待组合列表, 组合大小))函数来获取本次循环中要删除的边的组合,其中待组合列表为邻接矩阵e
中所表示的所有边,组合大小为i,即本次循环要删除的边的个数,e2del即为本次循环中要删除的边的各种组合 - 第二层循环,从e2del中取出待删除的边,进行删除,然后判断图的连通性,如果不连通则找到其中一个最小边割集,将其进行返回,否则对邻接矩阵
e进行复原,继续进行循环
- 使用
- 首先判断输入图是否为连通图
- 判断边连通度
1 | for edges in e2del: |
- 计算点割集的整体思想与计算边割集的思想一致,在
CalcTools.calc_vertex_connect()
方法中实现,该方法从少到多找出所有删除点的组合,然后对点和关联边进行删除,同时判断删除点和边之后的图的连通性,此处不再做过多解释
1 | def calc_vertex_connect(self): |
完整代码
绘图工具类
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
图计算工具类
1 | import copy |
主函数
1 | import numpy as np |
测试结果
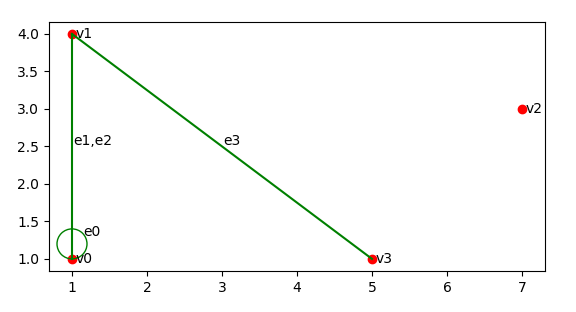
任务一
- 画出图G,并给所有顶点和边标号
- 输入点和边如下所示:
1 | v = np.array([[1, 1], [1, 4], [7, 3], [5, 1]]) |
- 绘图结果展示:
任务二
- 求出图G的度序列
- 输入点和边与任务一相同,度序列如下,与任务一展示图结果相对应,注:图中e1和e2为平行边
1 | # 任务二:图的度序列为[4, 3, 0, 1] |
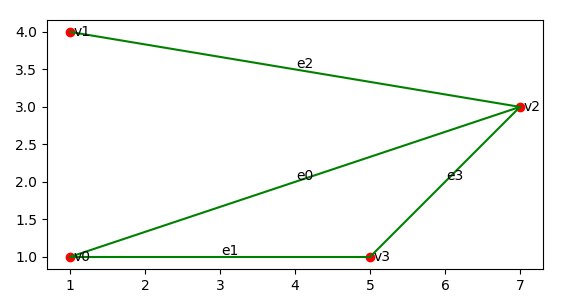
任务三
- 画出图G的补图
- 输入点和边与任务一相同,补图如下所示,与任务一的结果相对应
任务四
- 判断图G的连通性
- 输入点和边与任务一相同,运行方法判断图的连通性,结果如下所示:
1 | # 任务四:该图的连通性为False |
- 重新输入新的点坐标和边邻接矩阵,使新的图连通,如下所示
1 | # 接收点 |
- 重新输入图的展示与连通性判断结果如下:
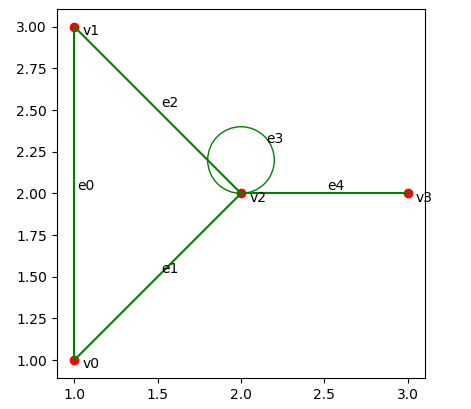
1 | # 任务四:该图的连通性为True |
任务五、六
- 求出图G的边连通度和点连通度
- 求出图G的最小点割集和最小边割集(元素最少)
- 输入的图如下所示:
1 | # 接收点 |
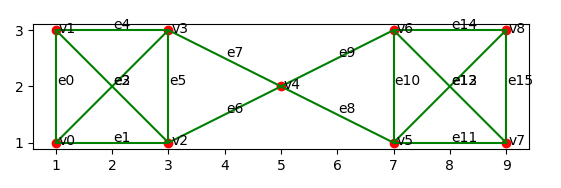
- 边割集/点割集,边连通度/点连通度计算结果如下:
1 | # 任务五、六:边连通度是2,最小边割集是[(2, 4), (3, 4)] |
- 其中边割集(2,4)表示从点v2到v4的边,即图中的e6,同理(3,4)表示图中的e7
- 点割集中的4表示图中的v4
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 PlanZ!





